Car Vibrations
Modeling vibrations of a car
Abstract
This article delves into the comprehensive analysis of car vibrations under average road conditions through the application of analytical and numerical methods. The project focuses on a full car model with seven degrees of freedom (DOFs) to capture the intricate vibratory behavior. By deriving equations of motion and utilizing simulations, the study aims to understand and mitigate car vibrations. The project uses a Mercedes CLS63-S AMG as a case study to showcase the approach.
Introduction
In the world of automotive engineering, understanding and minimizing vibrations experienced by a car under normal road conditions are paramount for comfort and performance. This project centers on analyzing the vibrations of a Mercedes CLS63-S AMG through both analytical and numerical techniques. The approach involves a detailed analysis of the car’s mechanical properties, leading to the derivation of equations that describe its vibratory behavior.

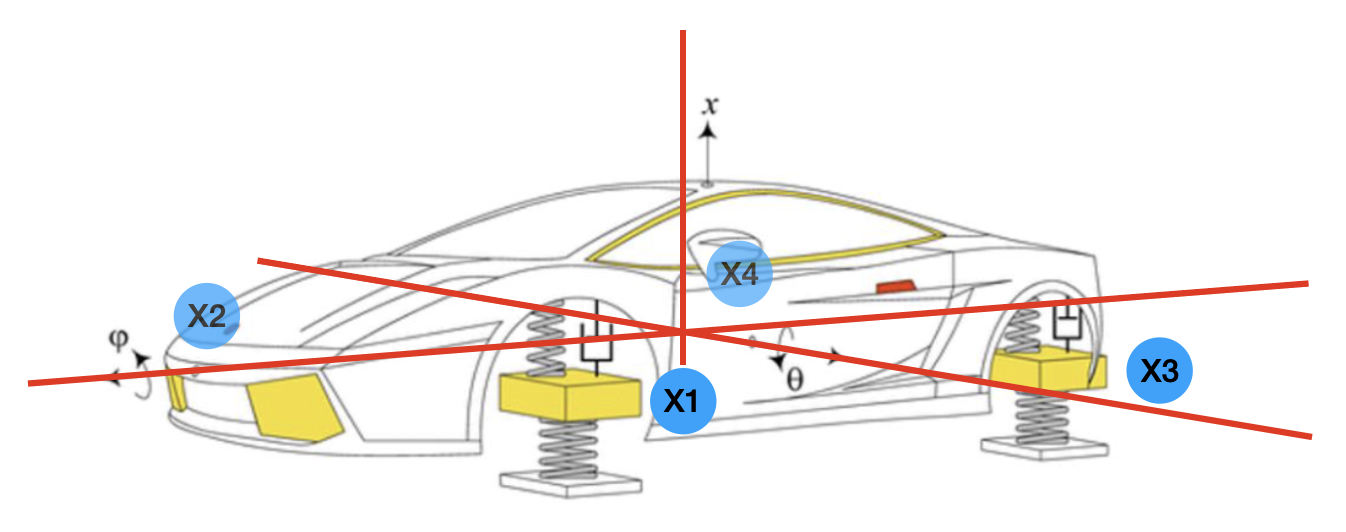
Identifying Degrees of Freedom
A pivotal aspect of this project involves identifying the degrees of freedom (DOFs) of the car. These are the independent variables that describe the car’s movement in different directions. For the Mercedes CLS63-S AMG, a full model with seven DOFs was employed, allowing a comprehensive analysis of the car’s behavior under varying conditions.
Deriving Equations of Motion
To understand the dynamics of the car’s vibrations, the Lagrange Energy Method was employed to derive equations of motion. This method takes into account kinetic, potential, and dissipation energies, resulting in a set of equations that provide insights into the vibrational characteristics of the car. This analytical approach forms the foundation for the subsequent simulations.
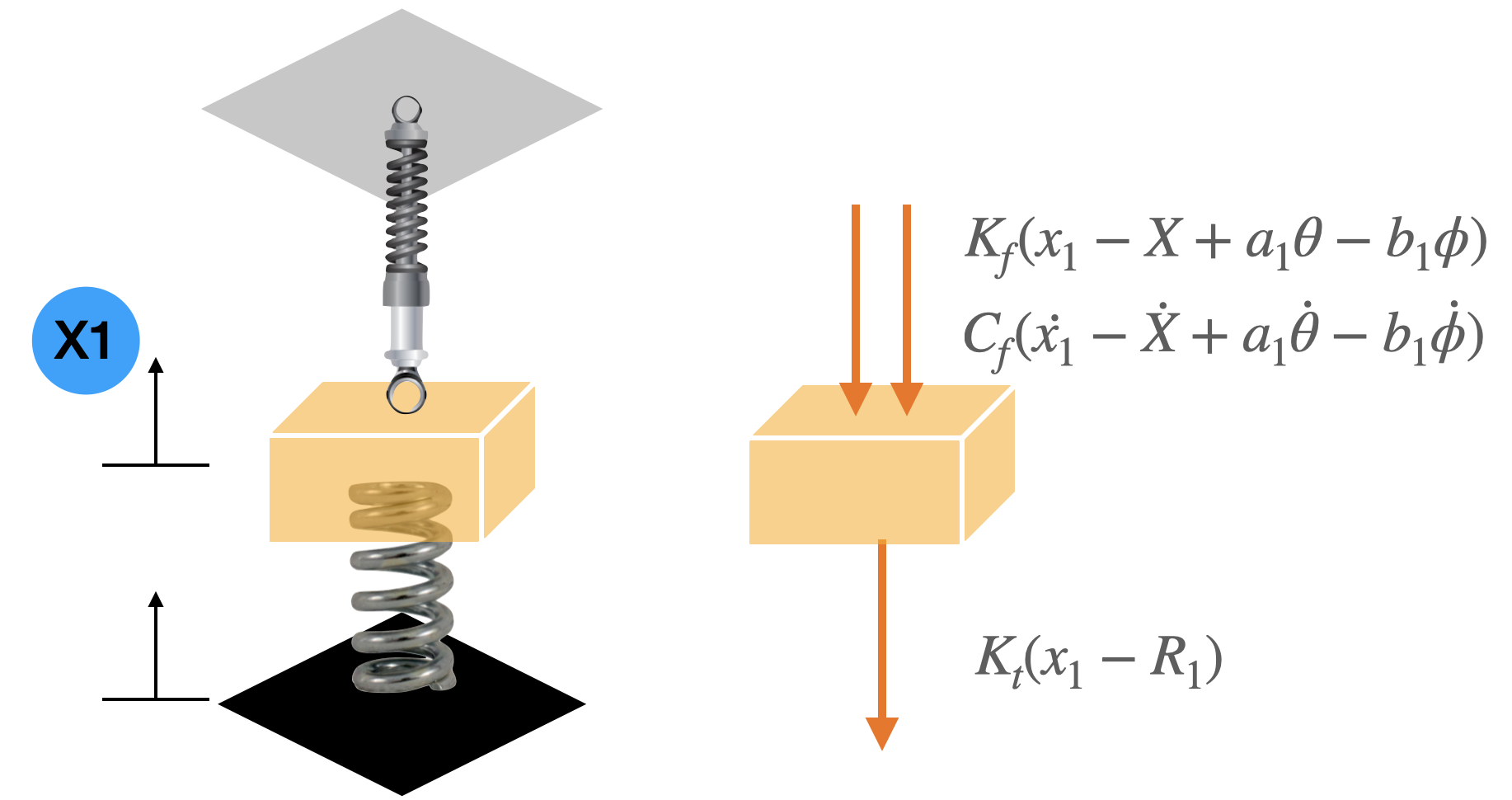
Chosen Parameters
Accurate modeling requires precise numerical parameters, which were sourced from established work in the field. The momenta of inertia, spring constants, and damping coefficients were calculated using a provided numerical calculator. These parameters serve as the building blocks for the subsequent simulations and analysis.
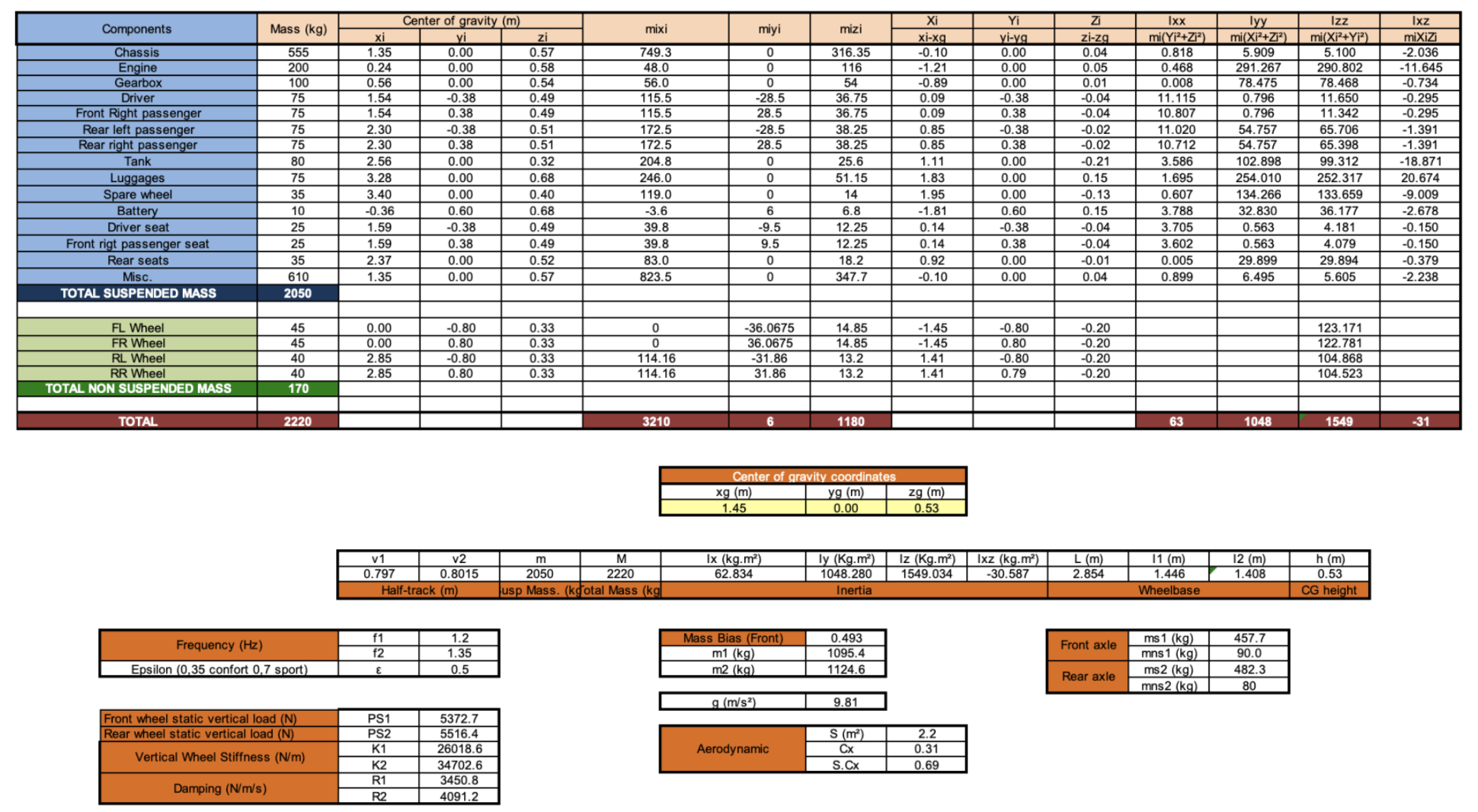
Details: Vehicle inertia calculation tool
Constant, C. (n.d.). Vehicle inertia calculation tool. Retrieved November 24, 2021, from here.
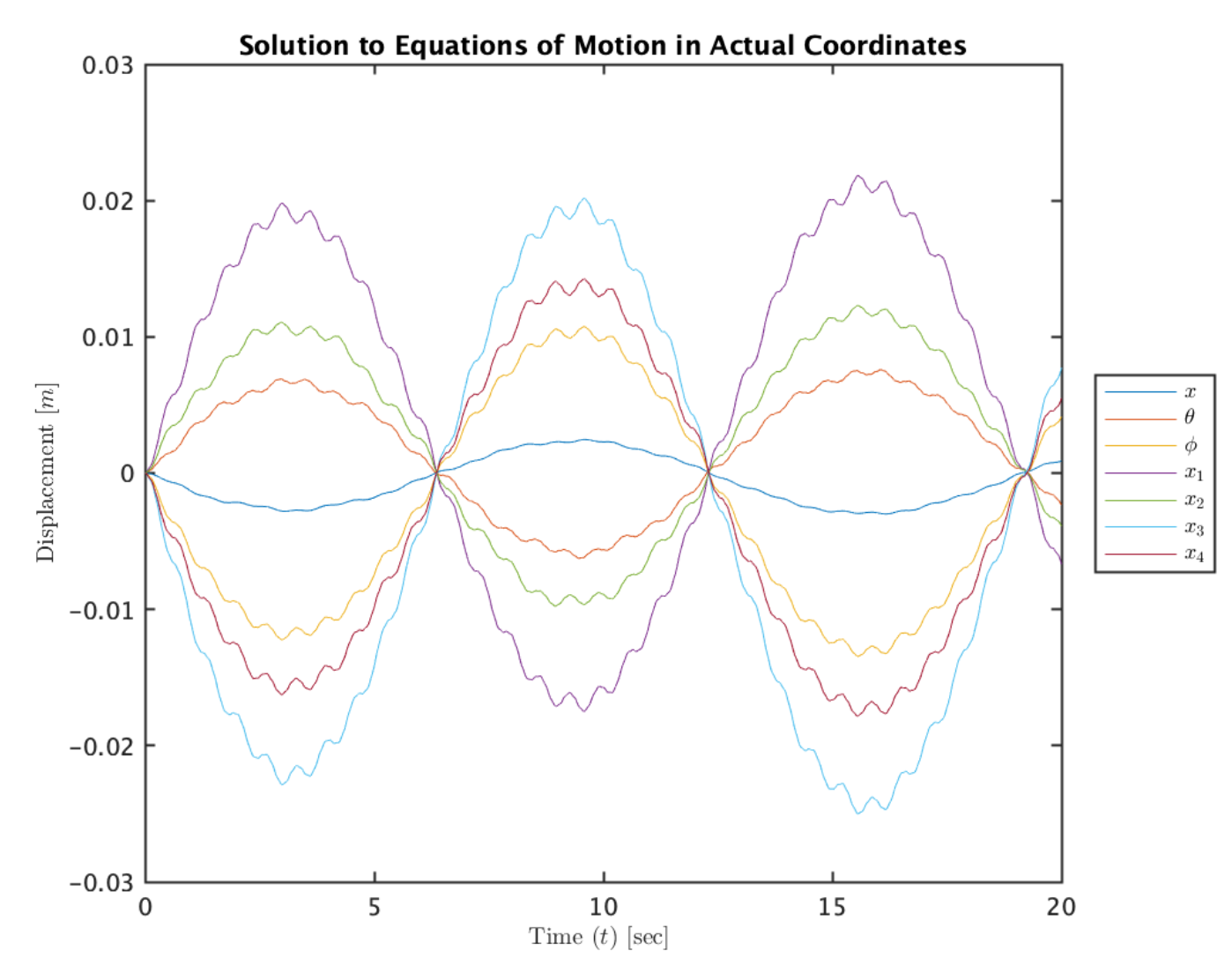
Simulation and Results
Utilizing the derived equations of motion and the chosen parameters, the project conducted simulations to observe the car’s response to road-induced forces. The simulations revealed intriguing patterns of vibration for each degree of freedom. Notably, the vertical displacement of the car’s body displayed the least vibration, acting as a buffer for the oscillations in the tire and suspension systems.
Conclusion and Future Work
The study highlights the importance of understanding and mitigating car vibrations for a smoother and more comfortable ride. The combination of analytical derivations and numerical simulations provides valuable insights into the dynamic behavior of the car under different conditions. While the optimization of damping coefficients remains a work in progress, the project underscores the potential for enhanced ride quality through systematic refinement.
In a world where automotive comfort and performance are paramount, projects like this pave the way for innovations that enhance the driving experience through a meticulous blend of theory, calculation, and simulation.